-By Hrishabh Sharma
About this article:
This article is not for making you master in this web development field but will definitely make you more comfortable…
Prerequisites:
No prerequisites buddy,be happy 😛
Just a Good text editor like Atom,Sublime Text 3 ,etc will be enough.
So let’s start this journey.
Let`s move on to a basic question:
How the websites work?
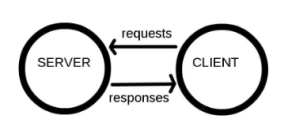
Computers connected to the web are called clients and servers. A simplified diagram of how they interact might look like this:
- Clients are the typical web user’s internet-connected devices (for example, your computer connected to your Wifi, or your phone connected to your mobile network) and web-accessing software available on those devices (usually a web browser like Firefox or Chrome).
- Servers are computers that store web pages, sites, or apps. When a client device wants to access a webpage, a copy of the webpage is downloaded from the server onto the client machine to be displayed in the user’s web browser.
The client and server we’ve described above don’t tell the whole story. There are many other parts involved, and we’ll describe them below.
For now, let’s imagine that the web is a road. On one end of the road is the client, which is like your house. On the other end of the road is the server, which is a shop you want to buy something from.
In addition to the client and the server, we also need to say hello to:
- Your internet connection: Allows you to send and receive data on the web. It’s basically like the street between your house and the shop.
- TCP/IP: Transmission Control Protocol and Internet Protocol are communication protocols that define how data should travel across the web. This is like the transport mechanisms that let you place an order, go to the shop, and buy your goods. In our example, this is like a car or a bike (or however else you might get around).
- DNS: Domain Name Servers are like an address book for websites. When you type a web address in your browser, the browser looks at the DNS to find the web site’s real address before it can retrieve the website. The browser needs to find out which server the website lives on, so it can send HTTP messages to the right place (see below). This is like looking up the address of the shop so you can access it.
- HTTP: Hypertext Transfer Protocol is an application protocol that defines a language for clients and servers to speak to each other. This is like the language you use to order your goods.
- Component files: A website is made up of many different files, which are like the different parts of the goods you buy from the shop. These files come in two main types:
- Code files: Websites are built primarily from HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, though you’ll meet other technologies a bit later.
- Assets: This is a collective name for all the other stuff that makes up a website, such as images, music, video, Word documents, and PDFs.
So what happens, exactly?
When you type a web address into your browser (for our analogy that’s like walking to the shop):
- The browser goes to the DNS server, and finds the real address of the server that the website lives on (you find the address of the shop).
- The browser sends an HTTP request message to the server, asking it to send a copy of the website to the client (you go to the shop and order your goods). This message, and all other data sent between the client and the server, is sent across your internet connection using TCP/IP.
- Provided the server approves the client’s request, the server sends the client a “200 OK” message, which means “Of course you can look at that website! Here it is”, and then starts sending the website’s files to the browser as a series of small chunks called data packets (the shop gives you your goods, and you bring them back to your house).
- The browser assembles the small chunks into a complete website and displays it to you (the goods arrive at your door — new shiny stuff, awesome!).
What is DNS?
Real web addresses aren’t the nice, memorable strings you type into your address bar to find your favorite websites. They are special numbers that look like this: 64.255.315.20.
This is called an IP address, and it represents a unique location on the Web. However, it’s not very easy to remember, is it? That’s why Domain Name Servers were invented. These are special servers that match up a web address you type into your browser (like “mozilla.org”) to the website’s real (IP) address.
After all this content that you have read you know briefly how web is working..
Now i think you are ready to learn the two different fields in this Web Development area and easily distinguish between them viz FRONTEND WEB DEV & BACKEND WEB DEV.
Basically,While frontend and backend development are certainly distinct from one another, they’re also like two sides of the same coin. A website’s functionality relies on each side communicating and operating effectively with the other as a single unit. Is one more important than the other? Nope. They both play very important roles in web development. So where should we start? Let’s flip a coin.
Frontend Web-Development:
The frontend of a website is what you see and interact with on your browser.
Let’s say you decide to start a business. You open a Vada Pav Shop 😂 and need a professional website to present your business to customers and tell them where you’re located. Maybe you’ll include a few photos and some information about your food items. All you need are frontend technologies to build your website.
Front-end Languages:
HTML,CSS,Javascript together create everything that’s visually presented when you visit a webpage — whether it’s online shopping, reading the news, checking your email or conducting a Google search.
HTML:
HyperText Markup Language is the language used to describe and define the content of a Web page in a well-structured format.
HTML consists of a series of elements, which you use to enclose, wrap, or mark up different parts of the content to make it appear or act a certain way. The enclosing tags can make a bit of content into a hyperlink to link to another page on the web, italicize words, and so on. For example, take the following line of content:
I Love Web-Dev
If we wanted the line to stand by itself, we could specify that it is a paragraph by enclosing it in a paragraph (<p>) element:
<p>I Love Web-Dev</p>
**keep in mind HTML is case insensitive ..
So,basically a HTML file consists of many such elements
A Simple HTML Code:
<!DOCTYPE html> <!--Declaration of HTML5 file --> <html> <title>HTML Tutorial</title> <!-- Title of the web-page --> <body> <!--contains body of the webpage or we can say that it is the section of the HTML document that will be directly visible on your web page. --> <h1>This is a heading</h1> <!--a simple heading tag --> <p>This is a paragraph.</p> <!--contains a paragraph --> </body> </html>
This is how a simple HTML code looks like..
If you want to experiment with writing some HTML on your local computer, you can:
- Copy the HTML page example listed above.
- Create a new file in your text editor.
- Paste the code into the new text file.
- Save the file as index.html
- Open it in web-browser .
You can explore many more tags and how to use them on:
https://www.w3schools.com/html/default.asp
CSS:
Cascading Style Sheets(CSS)) are used to describe the appearance of Web content.
The above one line may or may not have made sense, so let’s make sure things are clear by presenting a quick example. First of all, let’s take a simple HTML document, containing an <h1> and a <p> (notice that a stylesheet is applied to the HTML using a <link> element):
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>Page Title</title> <link rel=”stylesheet” href=”style.css”> </head> <body> <h1>This is a Heading</h1> <p>This is a paragraph.</p> </body> </html>
Now let’s look at a very simple CSS example containing two rules:
body {
background-color: blue;
}
h1 {
color: green;
text-align: center;
}
p {
font-family: verdana;
font-size: 20px;
}
The first rule starts with a body selector, which means that it will apply its property values to the <body> element and change background color to yellow.
The second rule starts with an h1 selector, which means that it will apply its property values to the <h1> element. It contains two properties and their values (each property/value pair is called a declaration):
- The first one sets the color text of heading h1 to green
- The second one modifies the text and align the text in center..
The third rule starts with a p selector, which means that it will apply its property values to the <p> element.
Now try it yourself,by applying css properties in your own web-page .
Take help from:
https://www.w3schools.com/css/default.asp
JavaScript:
JavaScript is the programming language that runs in the browser, which is used to build advanced interactive Web sites and applications for secure browser execution.
I will not go deeper in this ,as this is itself a huge topic,so wait might write on it in future..
In addition to basic front-end languages, you’ll come across frameworks like Bootstrap and Angular, as well as JavaScript libraries like jQuery, and CSS extensions like Sass and LESS. There’s a long list of resources like these, which support HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. Their purpose is simply to make code more manageable and organized by providing various tools and templates compatible with common coding languages.
Another interesting thing:
BOOTSTRAP:
According to the official website, Bootstrap is the most popular HTML, CSS, and JS framework for developing responsive, mobile first projects on the web.
Bootstrap can be boiled down to three main files:
- bootstrap.css – a CSS framework
- bootstrap.js – a JavaScript/jQuery framework
- glyphicons – a font (an icon font set)
Below is starter template for Bootstrap taken from official website or you can also download Bootstrap files on your system to access them offline instead using CDN as used below :
<!doctype html> <html lang="en"> <head> <!-- Required meta tags --> <meta charset="utf-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1, shrink-to-fit=no"> <!-- Bootstrap CSS --> <link rel="stylesheet" href="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.1.3/css/bootstrap.min.css" integrity="sha384-MCw98/SFnGE8fJT3GXwEOngsV7Zt27NXFoaoApmYm81iuXoPkFOJwJ8ERdknLPMO" crossorigin="anonymous"> <title>Hello, world!</title> </head> <body> <h1>Hello, world!</h1> <!-- Optional JavaScript --> <!-- jQuery first, then Popper.js, then Bootstrap JS --> <script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.3.1.slim.min.js" integrity="sha384-q8i/X+965DzO0rT7abK41JStQIAqVgRVzpbzo5smXKp4YfRvH+8abtTE1Pi6jizo" crossorigin="anonymous"></script> <script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/popper.js/1.14.3/umd/popper.min.js" integrity="sha384-ZMP7rVo3mIykV+2+9J3UJ46jBk0WLaUAdn689aCwoqbBJiSnjAK/l8WvCWPIPm49" crossorigin="anonymous"></script> <script src="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.1.3/js/bootstrap.min.js" integrity="sha384-ChfqqxuZUCnJSK3+MXmPNIyE6ZbWh2IMqE241rYiqJxyMiZ6OW/JmZQ5stwEULTy" crossorigin="anonymous"></script> </body> </html>
For more info on how to use it visit:
https://getbootstrap.com/docs/4.1/getting-started/introduction/
The grid is probably one of the most essential aspects of the framework. It’s the basis on which the entire layout is created. Beyond that, Bootstrap’s core CSS will also add helpful styling to forms, tables, buttons, lists, and images, as well as fully functioning navigation bars, while the core JavaScript will add helpful code for creating modals, alerts, popups, dropdowns, etc.
The Bootstrap grid system has four classes:
- xs (for phones – screens less than 768px wide)
- sm (for tablets – screens equal to or greater than 768px wide)
- md (for small laptops – screens equal to or greater than 992px wide)
- lg (for laptops and desktops – screens equal to or greater than 1200px wide)
So basically what Bootstrap’s grid feature does is that,it divides the whole screen into number of rows and 12 columns.
The following is a basic example of a Bootstrap grid:
<div class="row"> <div class="col-sm-4">.col-sm-4</div> <div class="col-sm-4">.col-sm-4</div> <div class="col-sm-4">.col-sm-4</div> </div>
The above example shows how to get a three equal-width columns starting at tablets and scaling to large desktops. On mobile phones or screens that are less than 768px wide, the columns will automatically stack.
Give your hands on by dividing screen into two unequal columns starting at tablets and scaling to large desktops,you will be more confident then.
So these grid classes automatically manages break points simlar to media queries in HTML5.
For more cool features and functionality of Bootstrap,You can visit:
https://getbootstrap.com/docs/4.1/layout/overview/
Backend Web-Development:
The backend (or “server-side”) is the portion of the website you don’t see. It’s responsible for storing and organizing data, and ensuring everything on the client-side actually works. The backend communicates with the front-end, sending and receiving information to be displayed as a web page.
Server Side Setup:
Your website needs a database to manage all the customer and product information. A database stores website content in a structure that makes it easy to retrieve, organize, edit, and save data. It runs on a remote computer called a server. There are many different databases that are widely used, such as MySQL, SQL Server, PostgresSQL, etc.
Your app will still contain frontend code, but it also has to be built using a language that a database can recognize. Some common backend languages are Ruby, PHP, .Net, and Python. These programming languages often run on frameworks that simplify the web development process. Django, for example, is a framework written in Python. “Django” is a popular technology for building dynamic web apps that makes the process much faster.
Ofcourse If you have learned basic HTML,CSS or have knowledge about little frontend then you can start learning Backend Web Development.
You can learn various Backend Platforms:
- Flask(Python)- http://flask.pocoo.org/docs/1.0/
- Django(Python)- https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/2.1/
- Ruby On Rails(Ruby)- https://rubyonrails.org/
- PHP- https://www.w3schools.com/pHP/default.asp
Frontend vs. Backend: Which Should I Learn?
If you’re keen to learn web development but aren’t sure whether to go down the frontend or backend route, it’s important to consider the day-to-day tasks of each. If you like the idea of working with visual designs and bringing them to life, creating a first-class user experience, then you’ll probably enjoy working in the frontend.
If you enjoy working with data, figuring out algorithms and coming up with ways to optimize complex systems, you might prefer to work as a backend developer.
Now you hopefully have a good idea of the differences between the frontend and backend, and how they work together to create functional, user-friendly websites.
I will surely write another blog on Backend Web-Dev soon..
So if you are interested start learning today.
Recommended Basic Courses:
https://in.udacity.com/course/intro-to-html-and-css–ud304
https://courses.edx.org/courses/course-v1:HarvardX+CS50W+Web/course/
The first course covers basic conecepts of HTML+CSS
And the second one deals especially with Backend Web Development Using Python
*Feel free to ask any doubts by leaving an email at
If you really like the content provided above ,then leave a like.😉
References:
For more info explore above mentioned link…